
What is seed funding?
Posted on 31st July 2023 by Phil Ainley
A quick guide to seed funding, what it is and how to access it
Seed money, also referred to as seed funding and seed capital, is a form of funding in which an investor invests their capital into a start-up in return for an equity stake or for a share in the profits of a product.
The term ‘seed’ suggests that it is very early investment which is meant to support the initial growth of business until it can of its own, or until it is ready for further investment.
Why would a business need seed funding?
A new start-up business may have limited access to funding and resources, and once the initial fees for company formation, computer hardware and software, materials, and office space (if required), are met, then there may not be a lot of money left over for the development of the business’s products and services.
At the start-up stage a business won’t have built up any trust or a credit rating with financial institutions. This can make accessing loans from bank and other investment portals very difficult.
Seed funding will typically be accessed to cover the initial costs of getting the business up and running, such as for developing a business plan and initial operating expenses including rent, payroll, business insurance, and even research and development costs (R&D).
Where does seed funding comes from?
A great proportion of the seed capital a start-up business raises typically comes from sources close to the company’s founders. These investors could be family, friends, or other acquaintances.
Seed capital is the first of five official funding stages that can help a start-up business become established.
It can be tempting as a founder of a start-up to accept the first deal that is presented to you, but seed funding is like any other business decision and takes time and thought to get it right.
Get your timing wrong and you could miss the boat and lose momentum if you’re late in seeking funding. However, if you’re too early you could damage your reputation. For example, you look for investment in a product which you haven’t tested yet, so you don’t know if it will work. Or you haven’t done your market research to see if there’s a market for your product.
Watch past episodes of Dragon’s Den and you’ll get a clearer picture of some of the mistakes that can be highlighted which could damage your reputation if you’re unprepared.
How do you choose how much seed funding you need?
The sum of funding that you might need will depend on your business, it’s products and services, and the long-term goals of the business.
As a start-up business owner, you might want to raise enough cash simply to grow enough take part in additional funding rounds. You may look to seek enough funding to become profitable. The choice is yours and will depend on your vision and ambitions for the business.
Where does seed funding feature in the funding timeline?
Seed funding only represents a single stage in a business’s funding cycle. Typically, it is the second stage in the cycle, with series funding stages following seed funding.
- The first stage in the funding cycle is known as pre-seed funding. Typically, pre-seed investments come at the very start of a company’s existence and this type of informal investment is rarely counted as an official funding stage.
- Seed funding is the second stage in the funding cycle but is widely regarded as the first official funding stage.
- Stage three in the funding cycle is Series A funding. The name Series A comes from the preferred stock that is sold to investors. For this stage, it’s crucial that you have a plan for developing a business model that will generate long-term profit. At this funding stage, investors are looking for more than just great business ideas, they’re looking for companies with a strong strategy that will turn their ideas into a money-making business.
- The fourth stage is Series B funding, which is typically about raising funds to take a business to the next level, past the development stage, and by expanding market reach. Businesses that go into Series B funding will have developed a user-base and proven to investors that they are prepared for growth and success on a larger scale.
- Series C funding comprises the fifth stage in the funding cycle, which is typically for successful businesses who are looking for funding to develop new products, expand into new markets, or even acquire other businesses, as part of their growth plans.
- After Series C funding, many businesses will complete an initial public offering (IPO), but some companies will still need to continue using fundraising rounds to grow. An IPO is the process of offering shares of a private corporation to the public in a new stock issuance for the first time, which allows a company to raise equity capital from public investors.
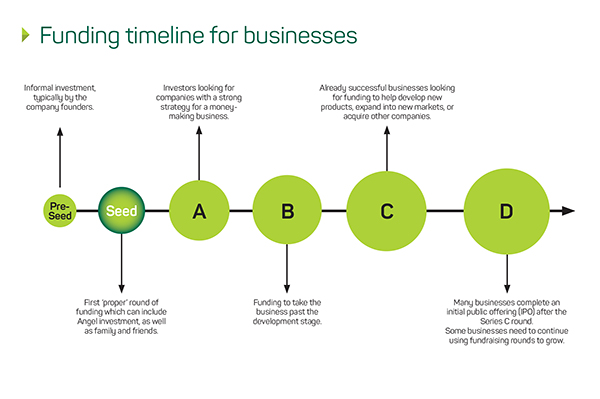
Funding timeline for businesses from pre-seed to IPO.
Funding round-up
Understanding the different funding rounds will help you understand and evaluate prospects for growth.
Each funding round operates in a comparable manner; investors offer cash in return for an equity stake in the business. For each round, the investors make different demands on the start-up.
Despite companies having different risk profiles and maturity levels at each funding stage, seed and Series A, B, and C investors all help business ideas come to fruition.
Series funding enables investors to support entrepreneurs with funds to fulfil their dreams, which can result in both the entrepreneur and the investor cashing out together at the IPO stage.
What other sources of business funding are there?
There are many different forms of funding for businesses of all sizes, including:
- Start-up and new business loans.
- Unsecured business loans.
- Secured business loans.
- Short-term loans.
- Business expansion loans.
- VAT and tax loans.
- Working capital loans.
- Bridging loans.
- Cashflow loans.
- Ring-fenced loans for female entrepreneurs.
- Bad credit loans.
- Government grants.
- Other grant funding initiatives.
- Business credit cards.
- Commercial mortgages.
- Business line of credit
- Revolving credit facility.
- Merchant cash advance.
- Asset finance.
- Invoice finance, factoring and discounting.
- Equipment and machinery finance.
- Trade and import finance.
- Peer-to-peer lending.
- Angel investments.
- Crowd funding.
- Finance options for niche types of business.
It is advisable to speak to your financial advisor or your business bank manager for further details if you are looking to secure commercial finance.
Disclaimer:
At Caunce O’Hara, we are passionate about helping small business thrive. Our content covers many topics you may find relevant and useful to your business. Please do not take this content as professional advice. To find out more on a subject we have covered in out articles, please seek professional assistance.
Sources:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Seed_money
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/seedcapital.asp
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/i/ipo.asp
www.businessfinancing.co.uk/business-funding/
https://www.barclays.co.uk/business-banking/business-insight/business-funding-options/
Useful Links

Professional Indemnity Insurance
Protects against claims of alleged negligence in your professional services, advice and designs.

Public Liability Insurance
Protects against claims of injury to third-parties or damage to a third-party's property.

Cyber Insurance
Covers your business in the event of a malicious attack on your computer systems and data.
